The 2024 UK Budget, introduced by Chancellor Rachel Reeves, is projected to raise £40bn of incremental revenue for the Treasury. Whilst changes were long signalled, now that the details have been released, DVS have explored how the specific changes around National Insurance may affect businesses in different sectors.
Given the Government chose to increase Employer’s National Insurance rather than Corporation Tax, this impact is higher on those with high wage bills. The structure of the changes to the lower threshold means that those with more staff on lower salaries will be harder felt.
Businesses are doing much of the heavy lifting in this budget, with £25bn on the £40bn raised coming from the 1.2% increase in employer NICs
- The gross pay threshold at which employer national insurance is paid decreases from £9100 per year to £5000 per year
- The percentage rate paid on gross pay above this amount increases from 13.8% to 15.0%
- Increasing hourly minimum wage from £11.44 to £12.21 will also represent a significant cost for businesses, particularly for those employing a high percentage of their workforce at or near the minimum wage
In terms of impact on payroll costs, the highest percentage increases will be felt in sectors with higher proportion of staff on minimum wage, and lower average salaries
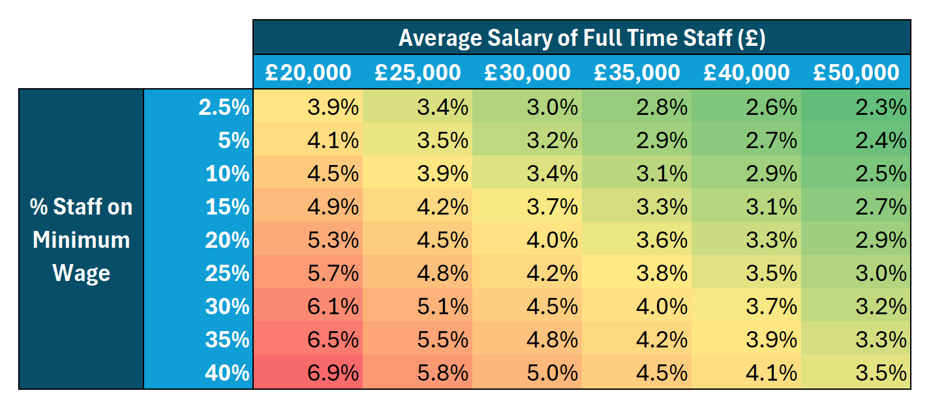
Figure 1. Increase in payroll costs by % of staff on minimum wage, and average salary of full-time staff overall
In practice, these changes will represent a 0.5-3.0% EBITDA (bottom line) headwind for most, with more labour-intensive businesses paying lower salaries hit hardest
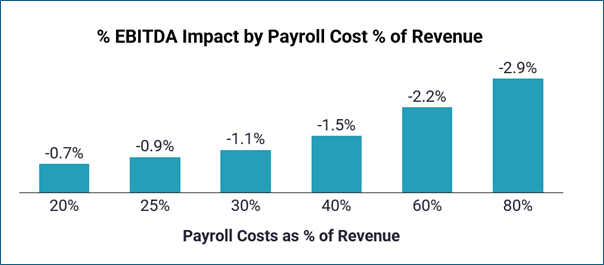
Figure 2. Change in % EBITDA bottom line by payroll cost as % of revenue (Assuming 15% of staff on minimum wage and average salary of £30000.
The implication of this is that some industries will be relatively more impacted by the changes in terms of their bottom line
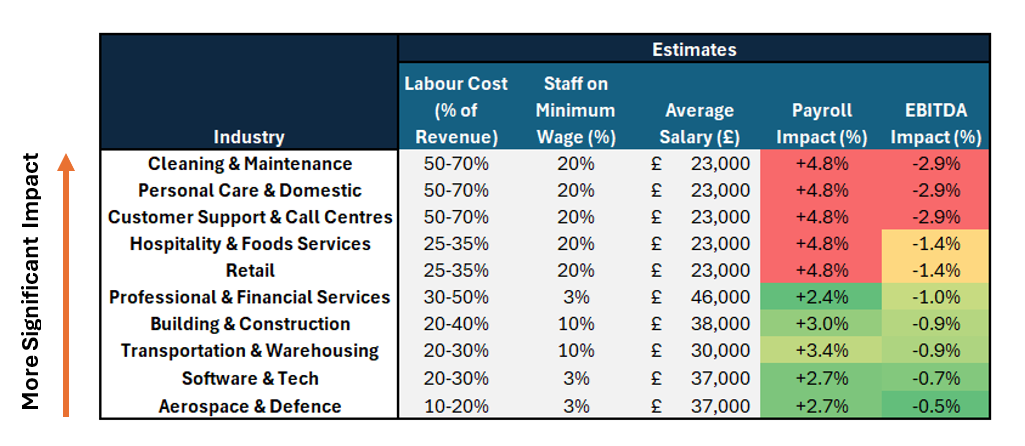
Figure 3. Estimated EBITDA impacted by industry (Assuming 15% of staff on minimum wage). N.B. a representative range of affected industries have been included here, with select industries broken out to highlight impact.
Low-wage, labour intensive industries like cleaning, care and customer support the most impacted by the changes in cost. Hospitality and retail payrolls are also increasing significantly by c.5%, but where the EBITDA impact is lower due to a lower labour cost burden.
There is a range of mitigations and strategies that should be considered by owners to prepare their businesses for these changes
- Operational Efficiency:
- Automation and Technology: Investing in automation can reduce reliance on labour, thereby minimising payroll expenses. We expect to see continued support for the use of AI in customer support and call centre roles
- Shift to Less Labour-Intensive Business Models: In retail for example, this is likely to further incentivise movement to online & omni-channel
- Financial Planning:
- Budget Reassessment: Revising budgets to account for higher payroll taxes and business rates is essential for maintaining financial health
- Tax Planning: Engaging in proactive tax planning can help identify opportunities to minimise tax burdens within legal frameworks
- Employee Compensation Strategies:
- Likely Impact to Wage Growth: Many employers may simply scale back planned pay increases to accommodate higher minimum wage and NIC contributions
- Staffing Structure Review: The reduction in the employer NIC allowance threshold from £9,100 to £5,000 may reduce the tax efficiency of employing multiple part-time workers instead of a single full-time employee
- Flexible Working Arrangements: This may incentivise companies to re-visit their hybrid or remote working policies to reduce overheads
Conclusion
The 2024 Budget introduces increased payroll costs and tax adjustments, which will undoubtedly present challenges for many businesses, especially those with higher labour costs and lower average compensation – such as Cleaning, Personal Care and Call Centres.
This likely provides a further catalyst for strategic and efficient transformation in impacted sectors including labour efficiency maximisation, strategy & process optimisation and deployment of artificial intelligence.

Sweeping US Tariffs: What This Means for the UK